An example of material development with NISHIYAMA Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Systems Engineering, Suwa University of Science
Development of Hard Coating Material Using Titanium Diboride Ultrafine Powder
X-ray analysis results
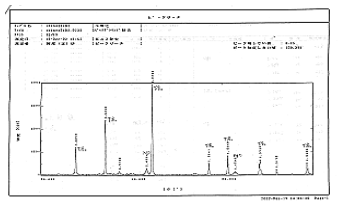
X-ray analysis indicates that titanium diboride (TiB2) could be formed with high purity.
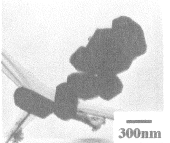
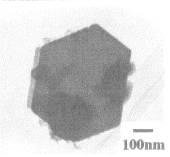
The generated titanium diboride (TiB2) can be seen as a platelet-shaped hexagonal crystal as shown in the electron micrograph.
Hexagonal plate crystal
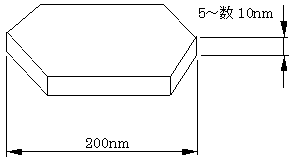
Characteristics of Titanium Diboride (TiB2) manufactured by MTR method
Nanometer-sized plate-like hexagonal crystals
- Very high hardness (approx. Hv.3400) (for reference: Hardened steel; Hv. 600-1000, Cemented carbides; Hv. 1500-2000)
- High melting point (2900°C)
- Chemical stability. Features of hardness, ultrafine particles, and plate-like crystals make it suitable for forming hard coatings.
Conceptual drawing of a plate hard film
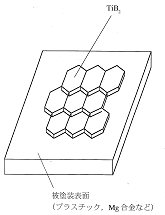
Hard coated section
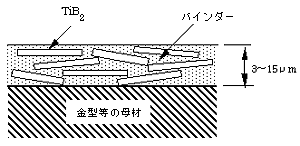
The high hardness of titanium diboride can be utilized by forming a protective film with TiB2 layered on the surface of the mold.